hexagonal bolt production process
What are the production processes of fastener products hexagonal bolts?
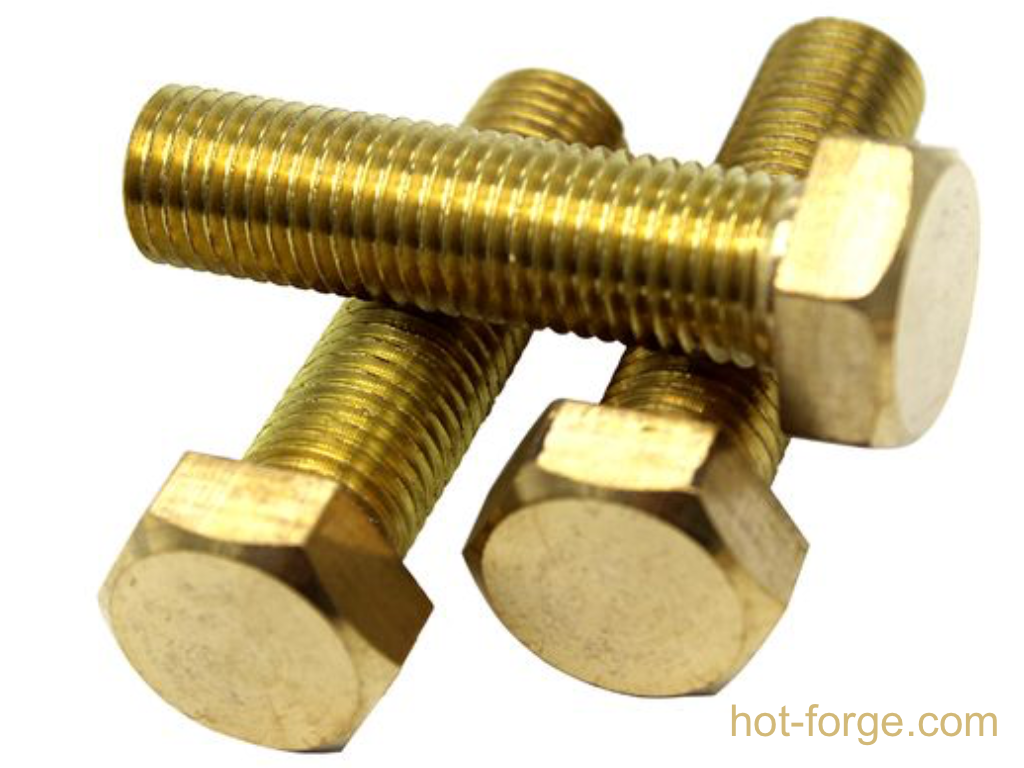
Hexagonal bolts are a common fastener and are widely used in machinery manufacturing, automobiles, aviation, and other fields. So, how are hexagonal bolts produced? The following is an introduction to the production process of our company’s production department.
1. Raw material preparation
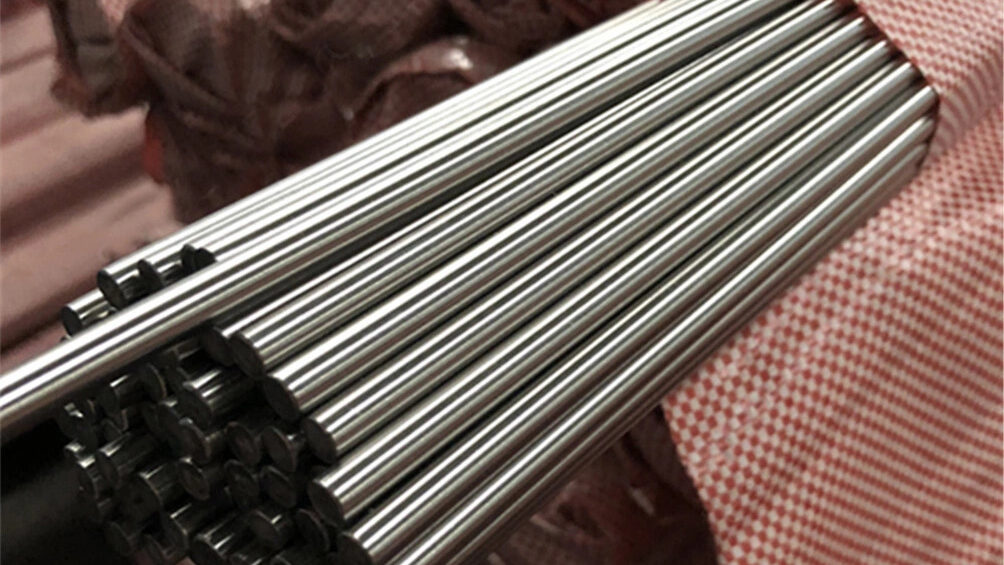

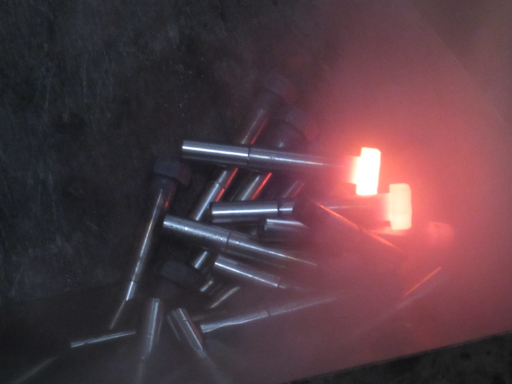
The raw materials of hexagonal bolts are mainly made of metal materials, which is the material range we operate (carbon structural steel, stainless steel, super duplex steel, nickel-based alloy, titanium alloy, copper alloy). First of all, it is necessary to purchase suitable materials. Before the raw materials are put into storage, the steel must be inspected and quality confirmed. Then carry out pre-processing work such as cutting and blank processing so that subsequent processing can proceed smoothly. The appropriate length of raw material is then forged. The preheated metal blank is put into the mold, and pressure and impact are applied at high temperatures to deform it to form the blank of the hexagonal bolt. The blank needs to remove hammer marks and surface oxide scale.
2. Processing and manufacturing
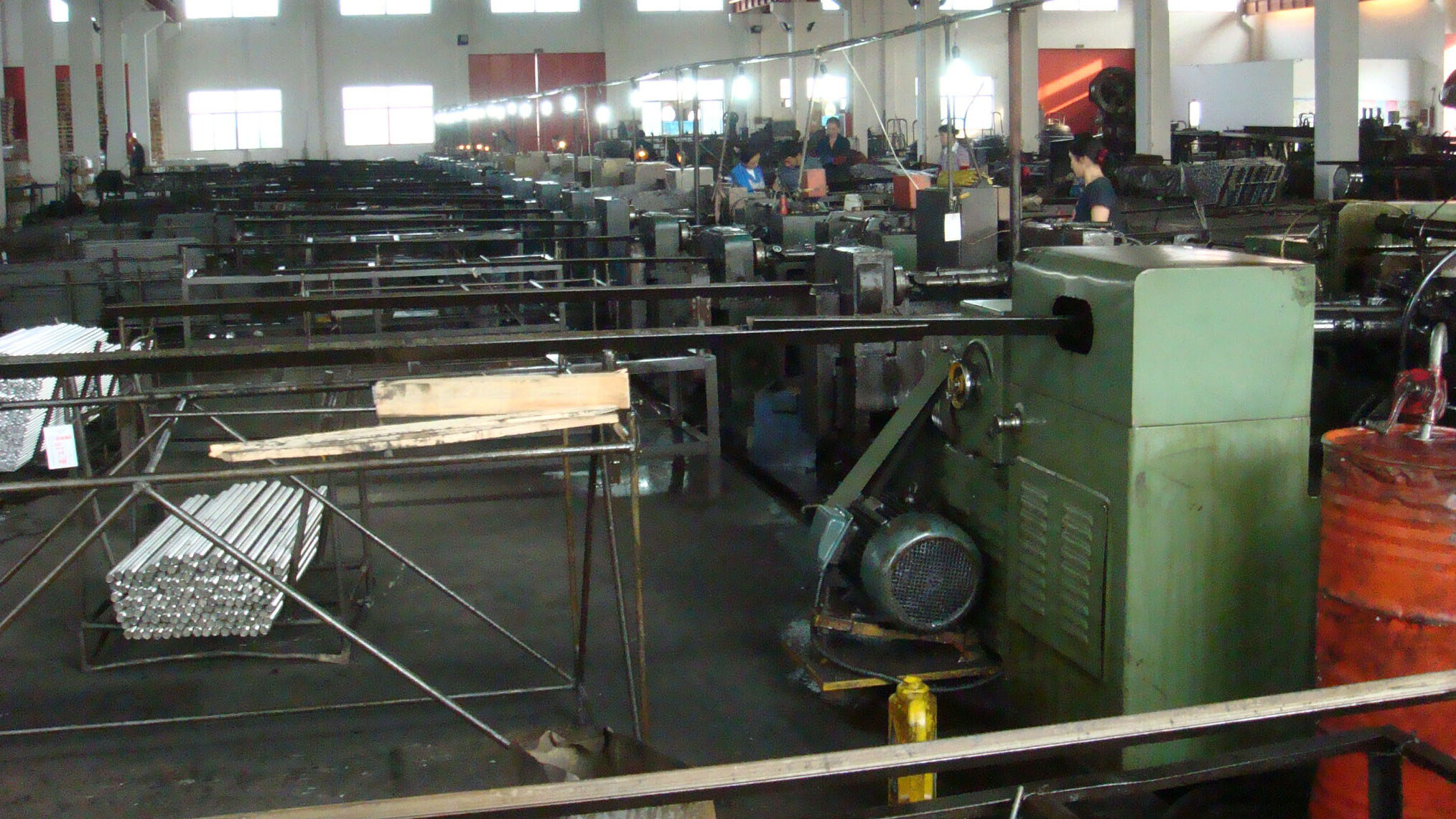

The pre-treated blank is heated to the appropriate temperature and then placed on the press for shaping. The forming of hexagonal bolts is usually divided into two methods: cold heading and hot heading. Cold heading is beneficial to improve production efficiency, while hot heading can improve the firmness and corrosion resistance of hexagonal bolts. After processing is completed, the finished products are inspected and screened by our QA.
3. Heat treatment

After completing cold or hot heading forming, the hexagonal bolts need to be heat treated. Heat treatment can increase the strength and hardness of hexagonal bolts, giving them higher tensile properties and wear resistance. This step is very important. We completely follow the heat treatment type and requirements in the material execution standards to ensure that the temperature meets the requirements. This process requires proper heating and cooling techniques to ensure the overall quality of the hexagonal bolts is reliable.
4. Processing threads

Threading is the use of mechanical equipment to process the outside or inside of a workpiece. It is usually divided into two types: internal threads and external threads. The main methods for processing threads include turning, milling, grinding, grinding, rolling, tapping and threading. Among them, thread rolling is a commonly used method in fasteners. It uses a forming rolling die to plastically deform the workpiece to obtain threads. Thread rolling is generally performed on a thread rolling machine or an automatic lathe equipped with an automatic opening and closing thread rolling head. It is suitable for mass production of external threads of standard fasteners and other threaded connections.
The advantages of thread rolling are as follows:
- The surface roughness is smaller than that of turning, milling and grinding;
- The strength and hardness of the thread surface after rolling can be improved due to cold work hardening;
- High material utilization rate;
- The productivity is doubled compared with cutting processing, and it is easy to realize automation;
- The rolling die has a long life. However, rolling threads require that the hardness of the workpiece material does not exceed HRC40; the dimensional accuracy of the blank is high; the accuracy and hardness requirements of the rolling mold are also high, making it difficult to manufacture the mold; it is not suitable for rolling threads with asymmetric tooth shapes.
5. Surface treatment
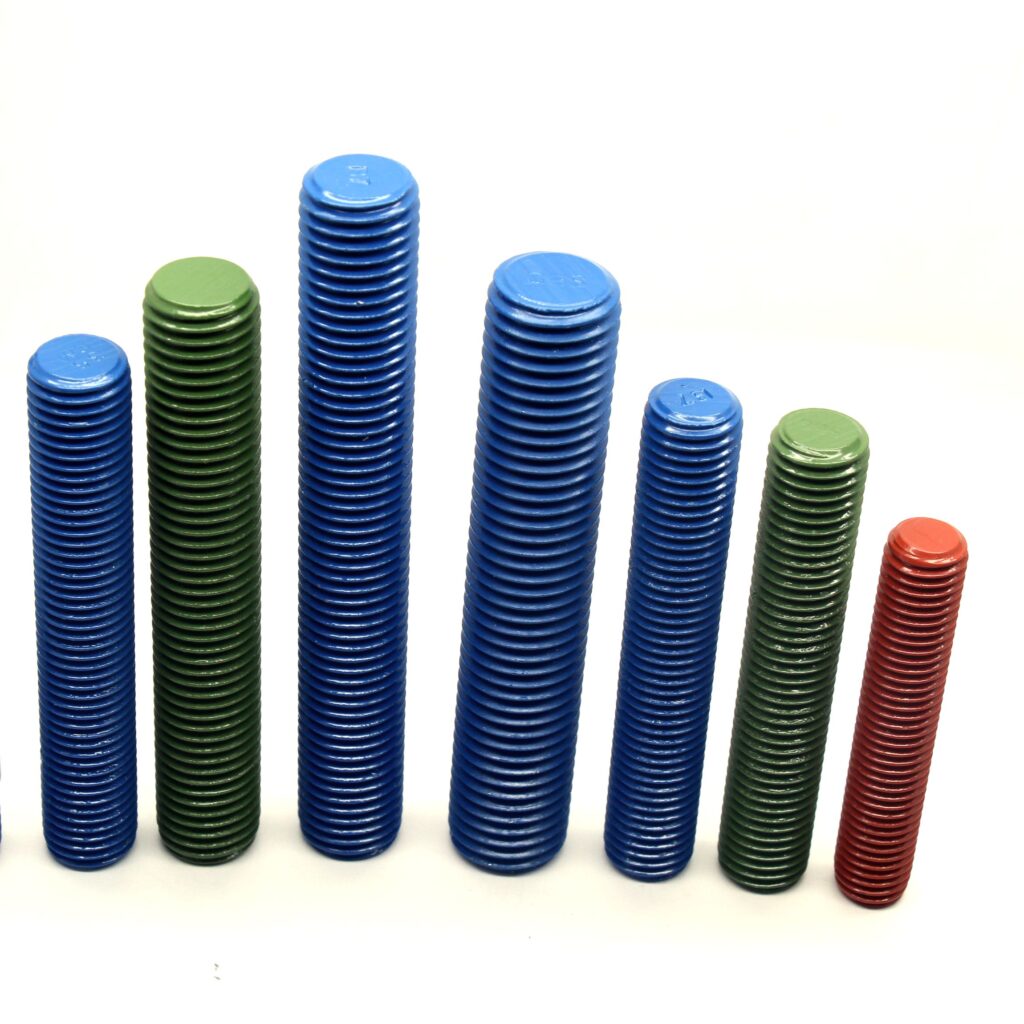
The surface treatment of hexagonal bolts is very important as it provides them with enhanced corrosion resistance, better anti-rust properties, decorative effects, etc. Surface treatment processes can be adopted (Hot Dip Galvanizing – standards ASTM A153, Electro Zinc Plating – standards ASTM B633, Teflon, PTFE-Xylan 1024/1070, Ceramic Filled Fluorocarbon Coating, Silver Plating – standards ASTM B254, GEOMET 321/720 – standards ASTM F1136, Electro less Nickel Plating – standards ASTM B733, Nickel Plating – ASTM B689, Electrodeposited Zinc Nickel Plating – standards ASTM B841, Cadmium-plated standards ASTM A165). Among them, the quality of surface treatment can affect the overall performance and appearance of hexagonal bolts.
6. Industrial testing

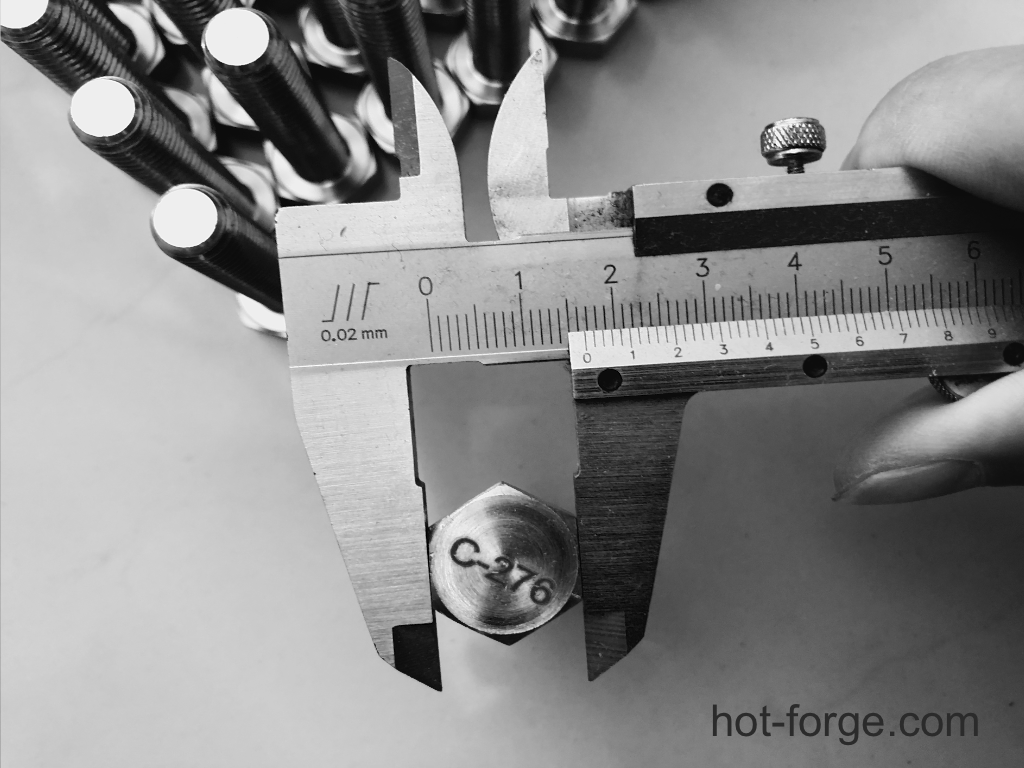
After production is completed, hexagonal bolts undergo a variety of inspection and testing processes to ensure that the product meets quality standards. Inspection content usually includes appearance inspection, dimensional inspection, tensile and torque strength inspection, etc.
7. Packaging
The final step is to package and deliver the hexagonal bolts. Packaging needs to use packaging materials and methods that meet the standard requirements of the target customer’s country to avoid damage to the goods during transportation and use and affect the import customs clearance progress.
In short, the production of hexagonal bolts is a multi-step process, each step of which requires careful operation and proper skills. Our workers have an average of 15 years of production experience. Only by strictly following the process can we ensure the stable quality, firmness and durability of the hexagonal bolts.